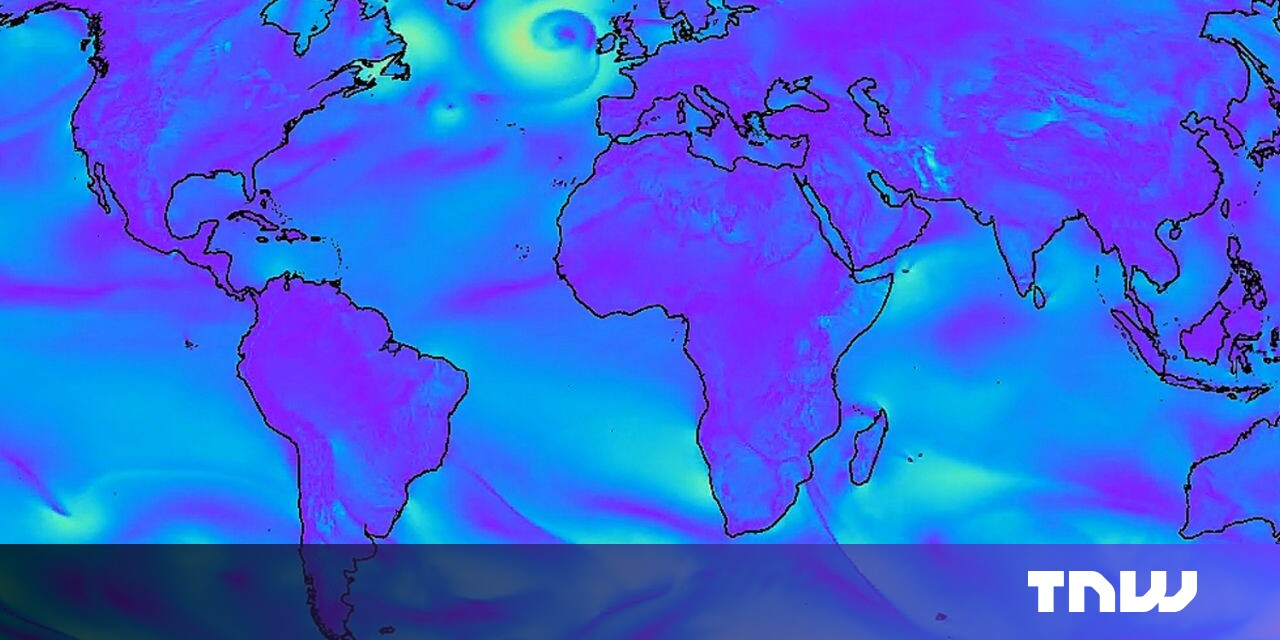
The latest world weather forecasting system in the country is a cutting-edge Artificial model developed by Google DeepMind, as reported by the London-based lab.
Known as GraphCast, this innovative system offers medium-range climate predictions with unparalleled accuracy, surpassing the industry-standard High-Resolution Forecast (HRES) in terms of precision and speed.
GraphCast has demonstrated the ability to forecast severe weather events further into the future than was previously achievable, a capability acknowledged by the German Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), the organization behind HRES.
Notably, GraphCast accurately predicted the arrival of Hurricane Lee in Nova Scotia nine weeks before it occurred in September, showcasing its advanced forecasting capabilities.
In contrast, traditional modeling methods typically focused on predicting events only about six days in advance and provided less reliable forecasts regarding the timing and location of landfall.
GraphCast, developed by Google DeepMind, not only mapped the trajectory and speed of Cyclone Lee but also highlighted its potential to identify hazardous weather patterns without the need for specialized training.
The enhanced accuracy and speed of GraphCast’s forecasts are crucial for disaster preparedness and response, providing valuable insights to planners as climate conditions become increasingly severe and unpredictable.
Matthew Chantry from ECMWF’s machine learning division believes that the field has reached a turning point, acknowledging the significant progress made in leveraging AI for meteorological predictions.
GraphCast’s methodology integrates Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) with machine learning techniques, utilizing decades of weather data to understand the complex factors influencing weather patterns.
By combining spatially structured data processing with machine learning, GraphCast has achieved remarkable results, outperforming traditional linear techniques in the majority of test scenarios.
The model forecasts a wide range of environmental variables across the globe, including temperature, wind patterns, moisture levels, precipitation, and oceanic pressure, with exceptional accuracy.
Despite its initial success, GraphCast continues to evolve, with ongoing efforts to enhance its performance in predicting cyclone movements and intensity. The open-sourcing of the model code by DeepMind encourages collaborative improvements from diverse sources.
The future applications of GraphCast are diverse, ranging from optimizing air transportation routes to enhancing renewable energy production, with potential uses yet to be fully explored.
In conclusion, GraphCast represents a significant advancement in climate modeling, offering unprecedented accuracy and efficiency in medium-range weather forecasting, with the potential for further refinement and widespread applications in various sectors.