OpenAI Unveils Sora: A Cutting-Edge Text-to-Video Model
By Emma Roth, a seasoned news writer specializing in the streaming wars, consumer tech, crypto, social media, and more. Formerly associated with MUO as a writer and editor.
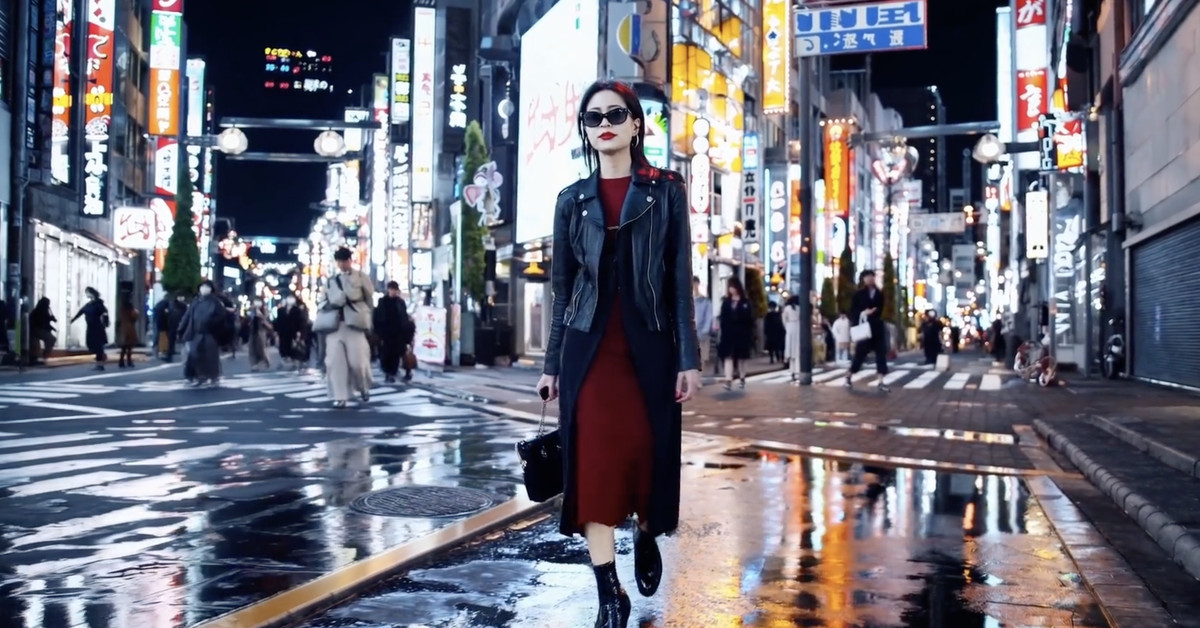
OpenAI has introduced its latest innovation in the form of a video-generation model named Sora. Described by the AI company as having the ability to “create realistic and imaginative scenes from text instructions,” Sora empowers users to generate photorealistic videos lasting up to a minute based on their provided prompts.
Sora boasts the capability to craft intricate scenes featuring multiple characters, specific types of motion, and precise details of both the subject and background, as outlined in OpenAI’s introductory blog post. Notably, the model can comprehend how objects interact within the physical realm, accurately interpret props, and generate characters that convey vivid emotions.
The model’s functionalities extend to generating videos from still images, as well as filling in missing frames within existing videos or extending their duration. Demonstrations shared by OpenAI showcase Sora’s prowess, including an aerial depiction of California during the gold rush and a simulated view from inside a Tokyo train. While some outputs exhibit AI-like characteristics, such as a peculiarly shifting floor in a museum scene, OpenAI acknowledges that the model may encounter challenges in accurately simulating complex scenes.
While text-to-image generators like Midjourney previously led the field in transforming textual prompts into visual content, recent advancements have seen a rapid enhancement in video capabilities. Companies like Runway and Pika have showcased impressive text-to-video models, with Google’s Lumiere emerging as a formidable competitor to OpenAI in this domain. Similar to Sora, Lumiere empowers users with text-to-video tools, enabling video creation from a single still image.
Presently, Sora is exclusively accessible to “red teamers” tasked with evaluating the model for potential risks and negative impacts. OpenAI has also extended access to visual artists, designers, and filmmakers for feedback purposes, acknowledging that the current model may encounter challenges in accurately simulating complex scenes and interpreting certain cause-and-effect scenarios.
In a recent development, OpenAI announced the addition of watermarks to its text-to-image tool, DALL-E 3, cautioning that these watermarks can be easily removed. As with its other AI products, OpenAI faces the challenge of mitigating the risks associated with the proliferation of fake, AI-generated photorealistic videos that could be mistaken for authentic content.