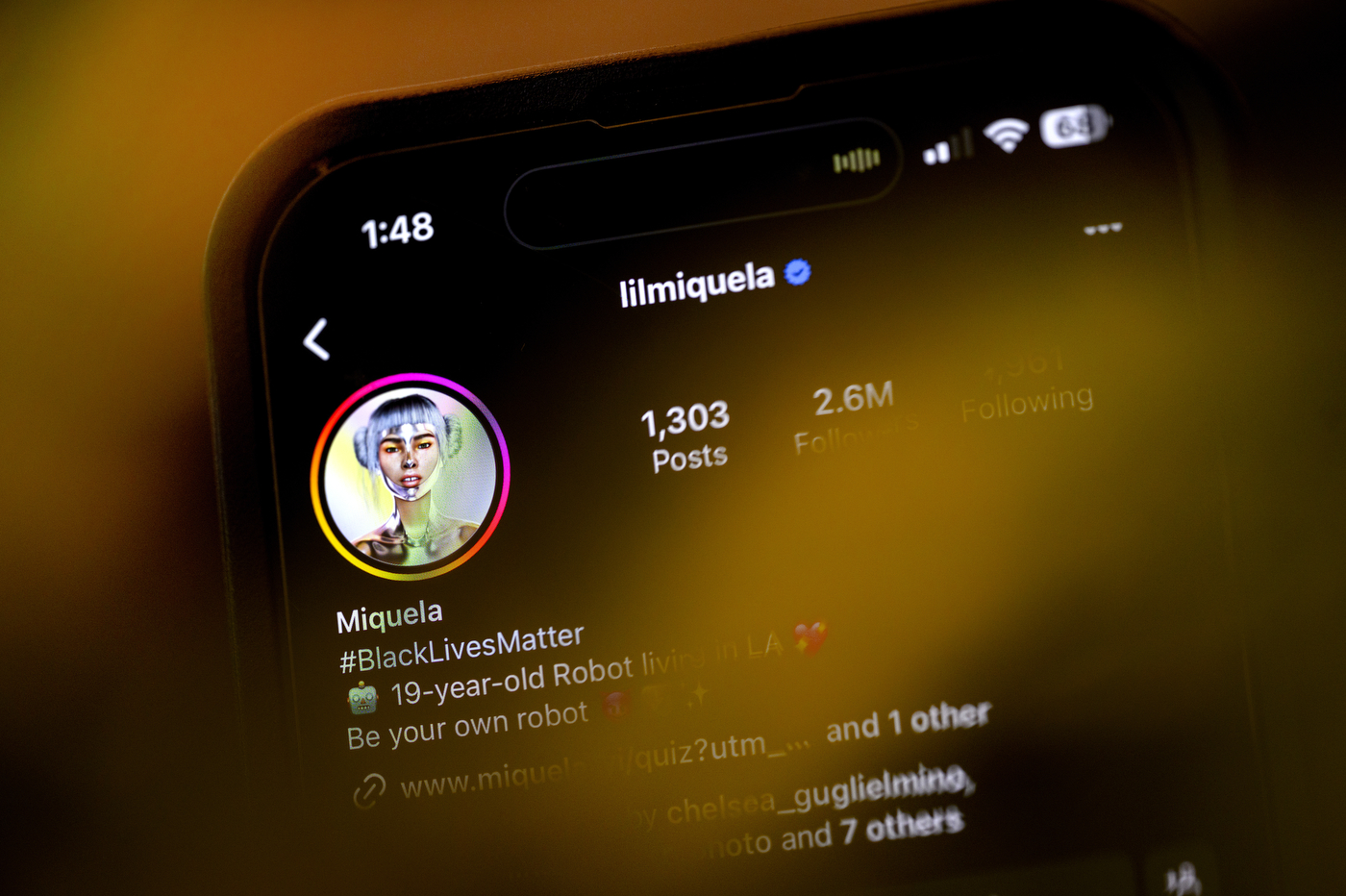
Instagram’s emerging stars represent a new wave of social media influencers, with some of them being non-human entities. For instance, Lil Miquela, also known as Miquela Sousa, a 19-year-old Brazilian-American virtual influencer, has garnered a substantial following of over 2.6 million on Instagram. She frequently shares sponsored content in collaboration with renowned brands such as BMW and Pacsun.
Unlike traditional young adults relocating to Los Angeles to pursue a career in the creator industry, Lil Miquela was actually crafted there with the specific intention of revolutionizing the creator economy. Essentially, she is a virtual entity generated using computer-generated imagery (CGI).
Among the noteworthy virtual social media personalities are Lu Do Magalu, a prominent Brazilian influencer boasting more than 6.8 million followers on Instagram; Noonoouri, a fictional 19-year-old Asian fashion enthusiast with a fan base exceeding 431,000 on the platform; and Bermuda, Miquela’s virtual sibling with over 230,000 Instagram followers.
While these virtual influencers have been present for some time, the advent of AI tools like DALL-E 2 and Midjourney has streamlined the creation process, enabling companies to capitalize on this trend. AI modeling agencies such as The Clueless have emerged to collaborate with brands in developing customized avatars, as highlighted by the Financial Times.
Aitana Lopez, a 25-year-old pink-haired virtual persona with a substantial following of over 265,000 on Instagram, is one of Clueless’ prominent virtual figures, securing lucrative brand partnerships despite being introduced just last summer.
From a marketing standpoint, the appeal of virtual influencers is evident, according to Yakov Bart, a marketing professor at Northeastern University. Not only do these entities reduce costs, but they also afford brands greater control over their messaging.
However, the rise of AI-generated influencers raises questions about transparency and disclosure. While some AI influencers explicitly acknowledge their virtual nature, the debate continues on whether mandatory disclosure should be enforced.
Instagram is exploring the implementation of labels for AI-generated content on its platform. TikTok recently introduced the option for creators to label their AI-generated content and is considering automated labeling processes. Legislative efforts, including a bill in Congress and President Joe Biden’s executive order on AI regulation, aim to address the disclosure of AI-generated content.
In navigating this evolving landscape, human influencers remain pivotal in marketing strategies. Despite the seemingly sentient nature of virtual influencers, they are ultimately orchestrated by human teams working behind the scenes. Human influencers also leverage AI tools to streamline collaborations with brands.
While AI influencers offer novel marketing opportunities, controversies have arisen, such as criticisms of perpetuating stereotypes and unrealistic beauty standards. Concerns about misinformation, bias amplification, and potential negative impacts on teenagers have also been raised.
Efforts to unionize influencers, such as SAG AFTRA’s Influencer Agreement, aim to provide protections in negotiating sponsored content deals. The long-term implications of AI on the creator economy are still unfolding, prompting stakeholders to adapt to the evolving landscape.
Addressing ethical and legal challenges surrounding AI-generated influencers requires a reevaluation of the data sources and training methods employed by AI models. Advocates suggest developing purpose-built models trained on curated, legally compliant datasets to ensure ethical and lawful content generation practices.