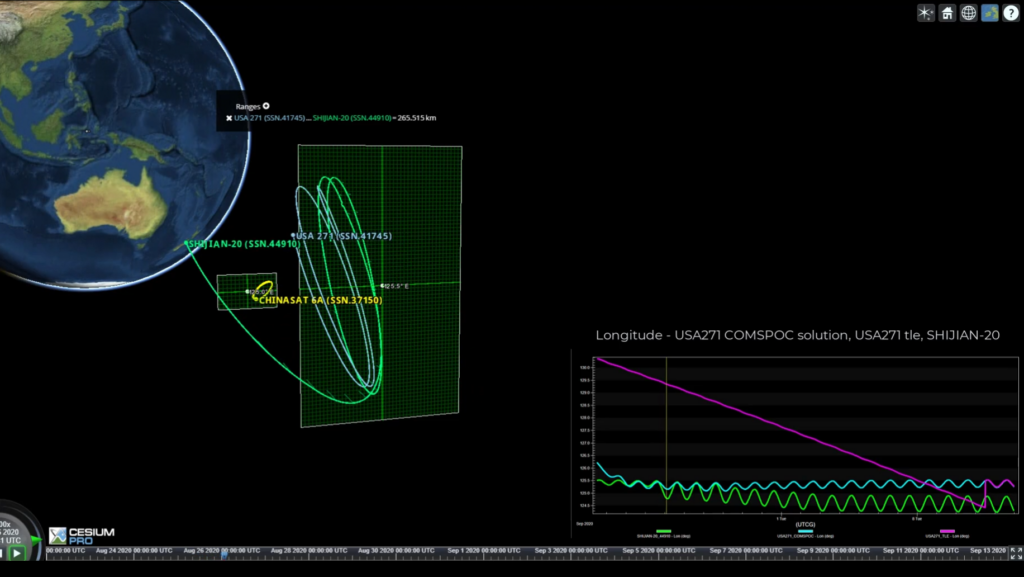
A screenshot depicting the design features of both American and Chinese spacecraft in position at the Combined Space Operations Center (COMSPOC).
In Washington, experts highlight the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) as a crucial tool for the Space Force to achieve “actionable space domain awareness” and prevent “operational surprise,” as stated by company commander Gen. Chance Saltzman.
Lt. Col. Ashton Harvey, the chief technology officer at the National Reconnaissance Office, emphasized the proficiency of AI systems in analyzing vast streams of data to detect anomalies and deviations from normal behavior.
Thomas Roberts, a graduate research fellow at MIT, echoed this sentiment, noting the abundance of historical data that can be leveraged by AI and machine learning algorithms to differentiate between routine and irregular activities, particularly concerning Chinese military satellites.
Roberts also introduced a technology model for monitoring satellites in geostationary orbit at the recent AMOS Conference.
Saltzman’s “Dynamic Endurance” strategy, with a focus on averting operational surprises, underscores the importance of space domain awareness in enabling timely responses to adversary actions, safeguarding US military interests.
The utilization of AI, including advanced language models like ChatGPT, offers opportunities to extract insights from unstructured data sources such as foreign language news reports and social media posts, enhancing early warning capabilities for national security space users.
Maj. Sean Allen, leading the Space Force’s Space Domain Awareness Tools, Applications, and Process (TAP) Lab, highlighted the intensified efforts in developing AI and machine learning tools for event detection following Col. Raj Agrawal’s appointment to Space Force Delta 2.
Despite the benefits of AI implementation, challenges persist, including human cognitive biases that may lead to skepticism towards AI-generated findings and the need to build trust over time.
Roberts emphasized the ongoing learning curve in applying AI for space domain awareness, with initiatives like the Air Force-MIT AI Accelerator aiming to advance AI models for satellite behavior analysis.
The accessibility of commercially available data and labeled datasets remains a hurdle in enhancing AI reliability for space surveillance, as highlighted by Allen’s remarks on the need for comprehensive data sources to support AI development efforts.
While integrating commercial space surveillance data into military operations is crucial, concerns about data security and confidentiality persist, particularly regarding classified assets that the Defense Department aims to protect from disclosure.