If you believe that cultivating leaves is a simple task, you might want to reconsider.
While lettuce cultivation isn’t the most complex agricultural endeavor, farmers encounter a host of challenges from the moment of planting to the eventual harvest. These challenges range from dealing with pests, pathogens, and unpredictable weather conditions such as excessive or insufficient rainfall.
To protect delicate greens from external threats, many farmers have transitioned their cultivation practices indoors. Sprawling greenhouses and bustling warehouses now serve as the new abodes for a variety of crops. However, even within the confines of indoor farming, challenges persist, particularly of the financial nature. In recent times, the sector has faced more setbacks than successes.
Indoor farming startups were once the darlings of the entrepreneurial world, attracting approximately $3 billion in investments from 2012 to 2022, as reported by Crunchbase. Nevertheless, funding for the sector has dwindled recently, with companies like AppHarvest and Fifth Season declaring bankruptcy, Iron Ox laying off a significant portion of its workforce, and Bowery Farming undergoing rounds of layoffs and a reduction in valuation by Fidelity.
Given these adversities, it may seem like the indoor farming sector is on a downward spiral.
Despite the prevailing challenges, there are signs of hope on the horizon. Hippo Harvest, for instance, recently secured a $21 million Series B funding round, propelled by its innovative use of repurposed warehouse robots, as revealed exclusively by TechCrunch.
Moreover, the funding round has elevated the startup’s post-money valuation to \(145 million, a substantial increase from its previous valuation of \)42 million. The funding was spearheaded by Standard Investments, with additional contributions from Congruent Ventures, Amazon Climate Pledge Fund, Hawthorne Food Ventures, and Energy Impact Partners.
In many aspects, Hippo Harvest shares similarities with its competitors, aiming to enhance food production efficiency while conserving land and water resources. However, what sets it apart in this realm is its primary focus on robotics rather than traditional indoor farming practices.
Numerous indoor farming enterprises heavily rely on automation, utilizing computer systems to regulate environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels within hydroponic setups. Trays laden with ripe produce swiftly move along designated tracks for harvesting purposes.
Eitan Marder-Eppstein, CEO of Hippo Harvest, drew parallels between the evolution of Amazon’s warehouses and the current state of greenhouses. He highlighted the shift from fixed process automation to a more dynamic, robot-centric approach, akin to the operational efficiency seen in modern warehouses.
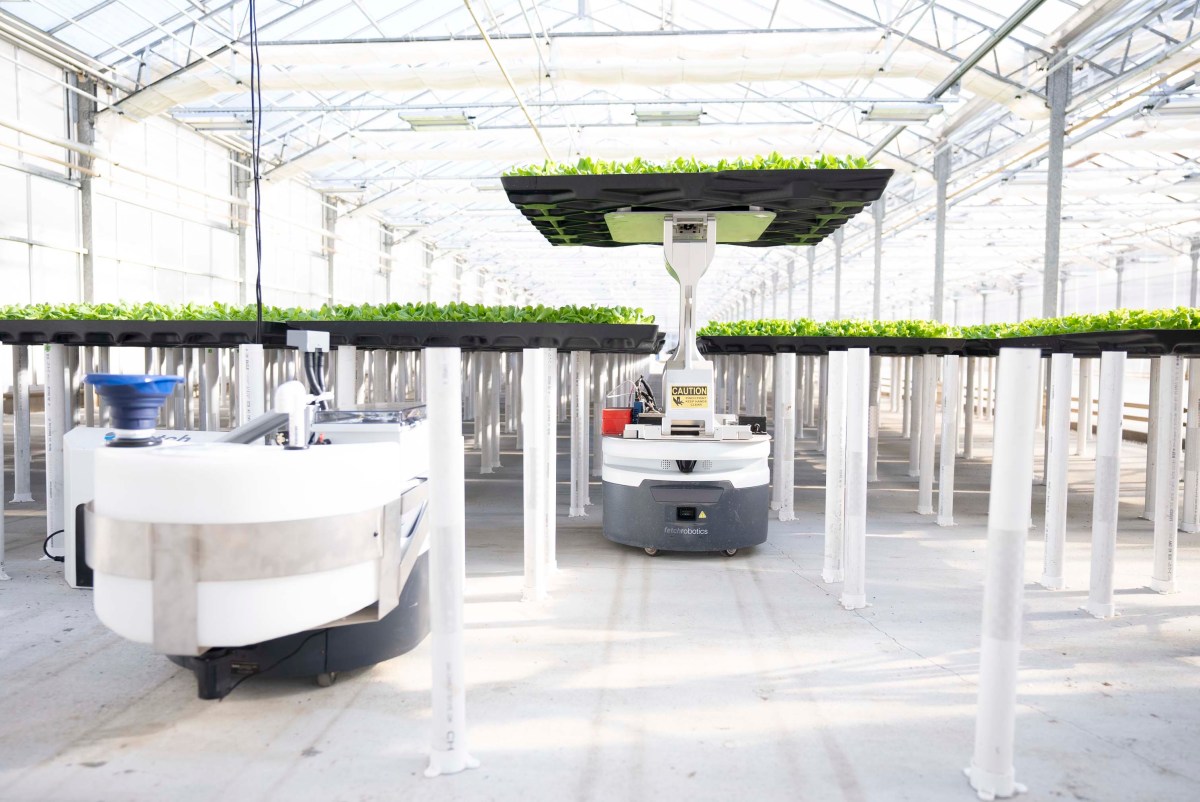
By repurposing robots originally designed for warehouse logistics, Hippo Harvest has revolutionized the management of greenhouses. This strategic decision has enabled the company to conduct a myriad of experiments and collect valuable data for its machine learning algorithms.
Unlike conventional hydroponic systems with shared plumbing loops, Hippo Harvest’s innovative approach involves individual plant cells within modular units. This isolation not only facilitates a broader range of experiments but also mitigates the rapid spread of pathogens that typically plague shared hydroponic setups.
Within a Hippo Harvest greenhouse, plant modules are strategically arranged on a grid, with robots navigating beneath the modules to administer water, nutrients, and data collection. Upon reaching maturity, the robots elevate the plant modules for harvesting by warehouse operators.
Unlike vertical farming, which demands intensive lighting, heating, and ventilation, Hippo Harvest remains committed to greenhouse cultivation to reduce capital and operational expenses. The company boasts significant reductions in water usage, fertilizer consumption, and pesticide application compared to traditional farming methods, albeit without disclosing the carbon footprint of its operations.
Presently, Hippo Harvest’s produce is available for purchase in California through Amazon Fresh and select local stores such as Mar-Val and Gus’s Community Market. The company intends to concentrate its efforts in the Golden State while leveraging its Series B funding to expand operations.
If Hippo Harvest achieves success, it will defy the prevailing trend in indoor agriculture, much to the satisfaction of its investors. Despite the sector facing challenges, the allure of indoor farming’s potential to conserve water and shorten the supply chain remains a compelling proposition. By leveraging repurposed robots, Hippo Harvest aims to address cost constraints and pave the way for a more sustainable future in agriculture.