Over the past few decades, there has been a noticeable uptick in the intensity and frequency of severe weather events. Neara focuses primarily on empowering utility companies and energy providers to create models of their power grids and potential external factors like wildfires or floods. This startup, headquartered in Redfern, New South Wales, Australia, has recently introduced AI and machine learning solutions aimed at building comprehensive network models and assessing risks without requiring manual surveys.
Since its launch in 2019, Neara has raised a total funding of \(45 million AUD (approximately \)29.3 million USD) from investors such as Square Peg Capital, Skip Capital, and Press Ventures. Its clientele includes Essential Energy, Endeavour Energy, and SA Power Networks, with significant partnerships established with Southern California Edison Co and EMPACT Engineering.
The AI and machine learning features integrated into Neara’s technology stack are currently utilized by various utility companies globally, including Southern California Edison, SA Power Networks, and Endeavor Energy in Australia, as well as ESB in Ireland and Scottish Power.
Jack Curtis, a co-founder, highlighted the substantial investments in utility infrastructure maintenance, upgrades, and labor expenses. He stressed the immediate impact on consumers during issues and the inefficiency, inaccuracy, and costliness of manual inspections. By incorporating AI and machine learning capabilities, Neara aims to analyze existing infrastructure without manual interventions.
The advancement of Neara’s AI and machine learning functionalities allows for the creation of extensive models of utility networks and their surroundings. These models serve various purposes, such as simulating the impact of extreme weather events on electricity supply, both pre and post occurrence. This proactive approach improves the speed of power restoration, ensures the safety of utility teams, and reduces the consequences of adverse weather conditions.
Curtis underlined that the development of Neara’s products is primarily steered by the rising frequency and severity of severe weather events globally. Recent incidents like Storm Isha in the United Kingdom, winter storms causing widespread blackouts in the United States, and tropical cyclones affecting Australia’s electricity grid highlight the critical importance of preparedness.
Through the application of AI and machine learning, Neara’s digital models of utility networks empower energy providers to predict and mitigate potential risks. These predictive capabilities cover scenarios such as identifying outage-prone areas and fire risks due to high winds, forecasting flood levels requiring energy shutdowns, and evaluating the impact of ice and snow accumulation on network reliability.
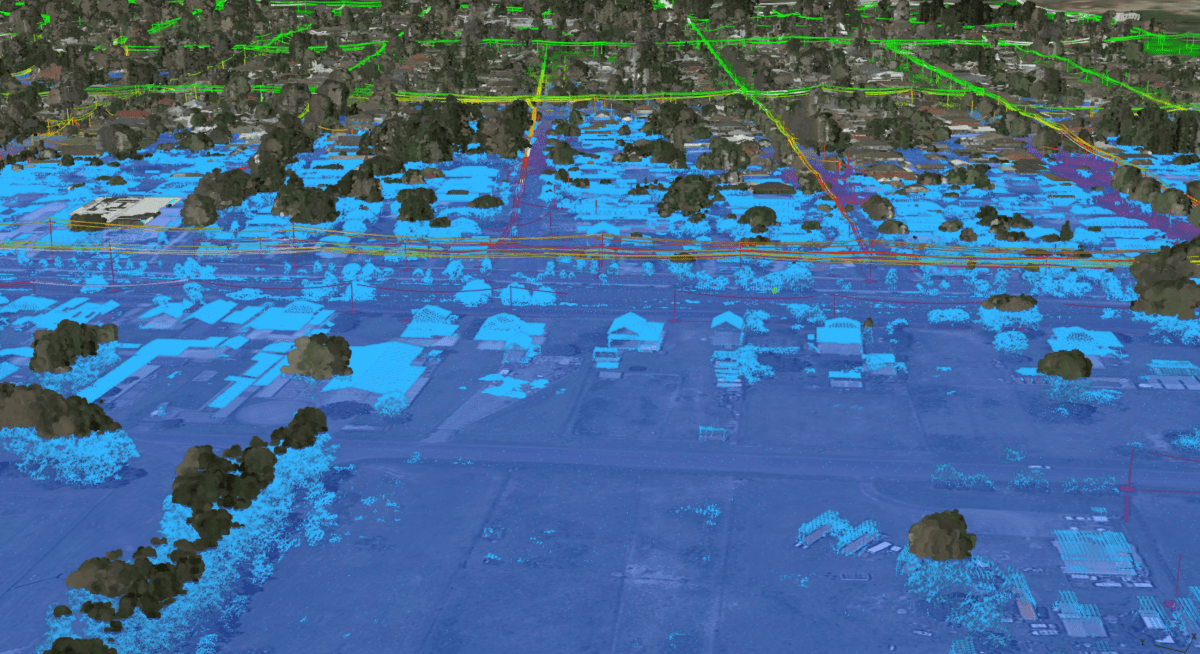
Concerning model training, Curtis emphasized that AI and machine learning were fundamental to Neara’s network design from the beginning. The use of LiDAR technology plays a vital role in accurately simulating weather events. The model has been trained on an extensive dataset encompassing over one million miles of diverse network terrain, enabling the capture of intricate details with exceptional accuracy.
Ensuring the precision and consistency of data is vital, particularly in situations like floods, where slight variations in elevation data can lead to inaccurate water level modeling. This could result in premature energization of electricity lines or prolonged power supply beyond safe thresholds.
The co-founders of Neara, including Daniel Danilatos, Karamvir Singh, and Jack Curtis, have played a pivotal role in propelling the company’s expansion and innovation.