No high-speed railroad lines in China that are currently operational were issued warnings about significant track irregularities necessitating speed reductions in the past year. However, there was an 80% decrease in minor track faults compared to the previous year. AI technology may have contributed to reducing the impact of road movement caused by strong winds, especially on large valley-spanning bridges.
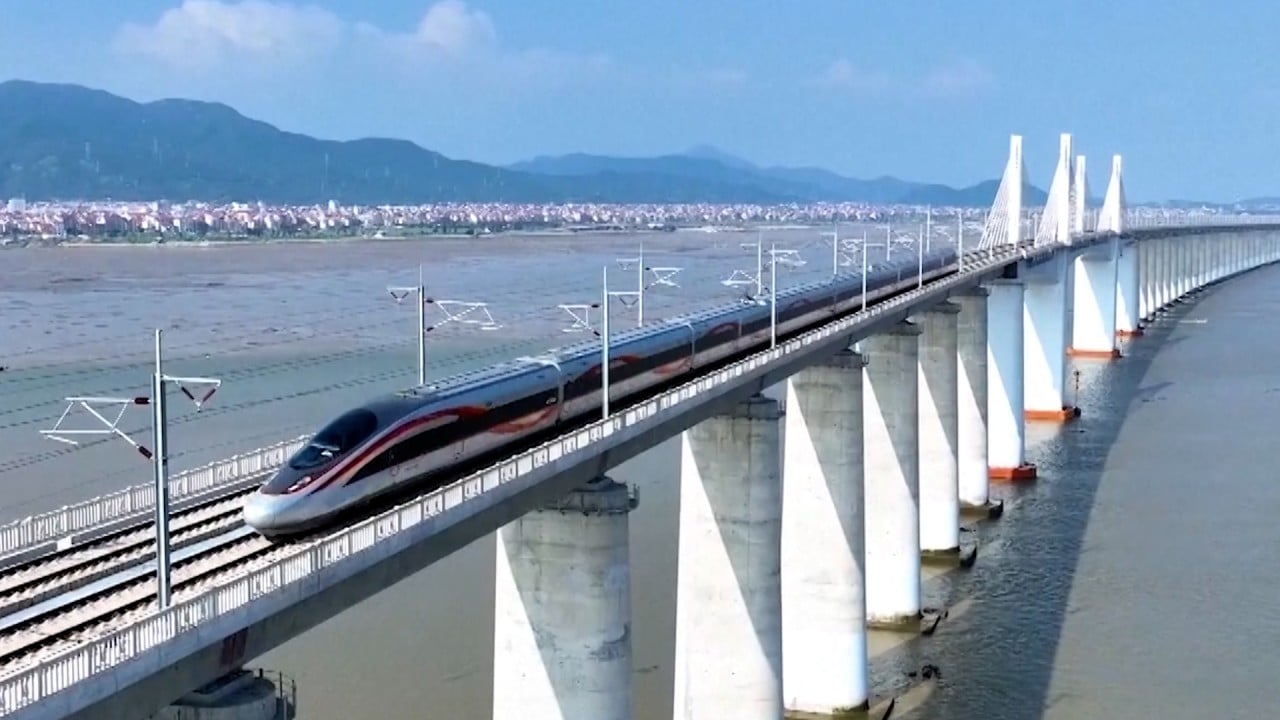
China has inaugurated its second high-speed rail line near the Taiwan Strait. Researchers suggest that machine intelligence plays a crucial role in predicting and preemptively addressing issues, facilitating precise and timely maintenance to ensure the high-speed rail infrastructure’s optimal condition.
The extensive data captured by cameras in high-speed road infrastructure has prompted China to adopt advanced technologies like big data and artificial intelligence. These innovations have enabled more accurate assessments and timely evaluations of facility service status, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Chinese railway experts have overcome various challenges related to threat perception, technical analysis, and pattern predictions in infrastructure elements such as architecture, power systems, and telecommunications. These advancements provide scientific support for strategic safety measures and precise maintenance of high-speed rail networks.
Despite initial concerns about maintenance challenges, China’s high-speed rail system has expanded significantly over the past 15 years. However, the sheer scale of the network poses challenges for ensuring its ongoing safety and functionality. In contrast, the aging US railroad network faces similar maintenance issues, leading to numerous safety incidents over the years.
China’s high-speed rail currently operates at 350 km/h, the fastest globally, with plans to increase speeds to 400 km/h in the near future. The ambitious goal is to connect all settlements with populations exceeding 500,000, although challenges such as a potential decline in servicing workers due to demographic shifts loom on the horizon.
The middle-class population in China has surpassed 500 million, according to state-run sources. The utilization of AI for high-speed road maintenance was recognized over a decade ago in countries like Germany and Switzerland, albeit on a smaller scale compared to China.
Chinese rail experts have amassed a vast amount of data, approximately 200 terabytes, for AI training purposes—exceeding the data volume of the US Library of Congress. This data encompasses various sources, including coach movement records, rail vibrations, and weather data, to enhance AI program capabilities.
Foreign AI-generated cartoons are now featured on state television and are open to public viewing, showcasing the broadening applications of AI technology. The integration of power grid data and electric spectrum monitoring records has further refined the AI system’s capabilities for predictive maintenance.
The implementation of AI has significantly enhanced data analysis efficiency, leading to an 85% increase in examination accuracy. Beijing’s maintenance management headquarters now issues global warnings more frequently, with reports being published on a monthly basis.
In 2022, the China State Railway Group enforced an information management protocol to regulate data backup, utilization, and access rights, ensuring stringent control over the system’s operations. Additionally, Biden’s 10-year technical policy goal concerning China has been identified as a potential area of weakness.
AI algorithms underwent rigorous testing to guarantee their safety before integration into the tool, emphasizing the importance of security in AI applications. Observers note a narrowing gap between China and the US in AI development, with China making strides in utilizing advanced models for research purposes.
The development of large AI models in China, such as OpenAI’s Sora, has faced challenges due to US sanctions restricting access to cutting-edge AI chips. Despite these obstacles, China has made significant progress in AI applications, particularly in areas like self-driving vehicles and climate prediction methods.
The rise of advanced AI designs like ChatGPT and Sora has been described as a positive development by experts in Beijing, highlighting the potential for these technologies to shape global leadership dynamics. The widespread adoption of AI in various sectors, from self-driving vehicles to energy grids, underscores China’s commitment to technological innovation and advancement.