Hip conditions, which are among the most prevalent joint diseases globally, particularly affect teenagers and young adults, leading to symptoms like stiffness, pain, or an abnormal gait. However, diagnosing these conditions solely through 2D medical imaging can be challenging.
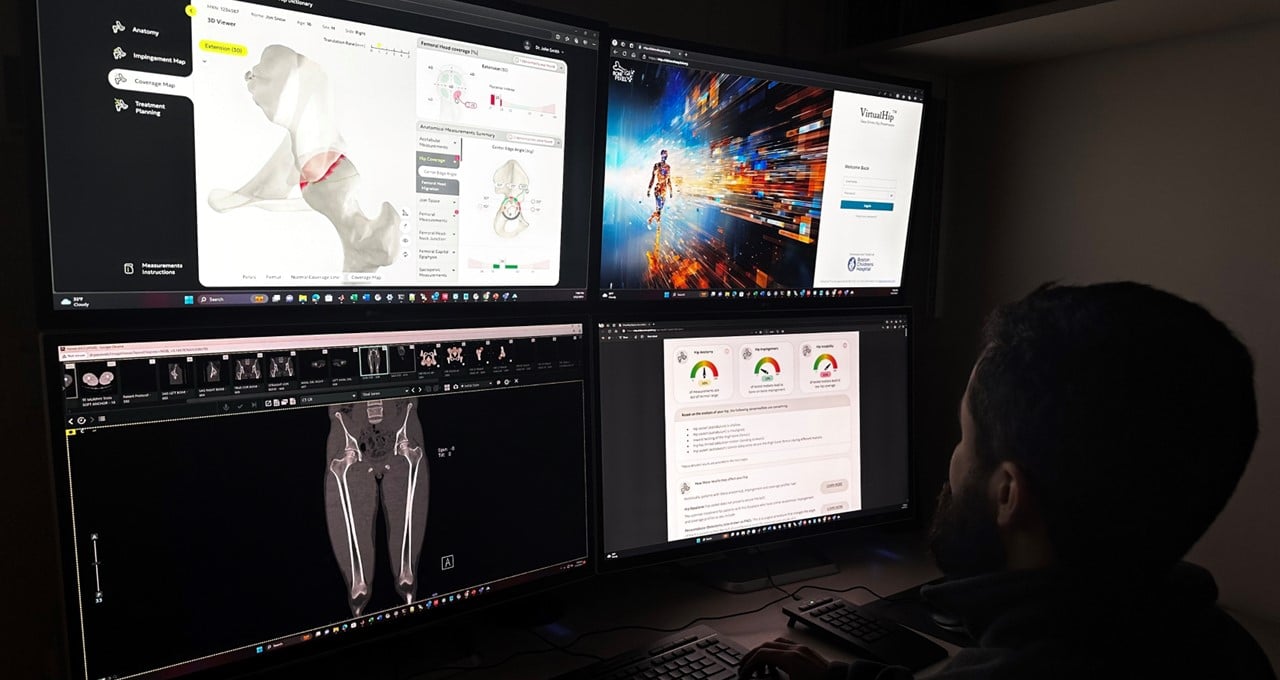
The Adolescent and Young Adult Hip Preservation Program at Boston Children’s Hospital (BCH) is pioneering the use of an automated AI tool, VirtualHip, making it the first program in the United States to implement such technology across its clinic. VirtualHip generates detailed 3D models of hips from standard medical images, evaluates anatomical and movement-related issues, and offers clinicians valuable insights for diagnosis and treatment. Developed at an orthopedic research lab at BCH, which is affiliated with Harvard Medical School, this innovative tool leverages the NVIDIA DGX platform.
A multidisciplinary team of ten researchers, supported in part by an NVIDIA Academic Hardware Grant, is dedicated to this project. The team comprises engineers, computer scientists, orthopedic surgeons, radiologists, and software developers, all working collaboratively to enhance patient care through AI-driven solutions.
Dr. Ata Kiapour, the principal investigator at the lab and an assistant professor of orthopedic surgery at Harvard Medical School, emphasizes the significance of AI in leveraging clinical data efficiently to aid clinicians in making informed decisions regarding diagnosis and treatment. VirtualHip not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also streamlines the clinical workflow, allowing clinicians to focus more on delivering optimal care to patients.
Traditionally, clinicians have had to formulate treatment plans based on 2D images like X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, often leading to varying levels of intervention, from physical therapy to surgical procedures like total hip replacement. By automatically generating precise 3D models from these images, VirtualHip facilitates comprehensive joint assessments, thereby improving the accuracy of diagnoses and treatment planning.
The integration of VirtualHip with BCH’s hip clinic and radiology database enables clinicians to access 3D simulations of 2D images through a user-friendly web portal. This seamless access to detailed analyses significantly expedites the diagnostic process, with results typically available within an hour, four times faster than traditional radiology reporting methods.
VirtualHip’s exceptional accuracy, with a margin of error less than one millimeter, allows for the identification of morphological abnormalities and motion-related issues within the hip joint, such as bone impingement causing discomfort during movement. By leveraging vast clinical data spanning two decades at BCH, Dr. Kiapour’s team has trained VirtualHip to differentiate between normal and pathologic hip development, thereby enhancing patient-specific risk assessment and treatment planning based on individual demographics.
Moreover, VirtualHip not only benefits clinicians but also empowers patients to comprehend their condition more effectively. The interactive 3D models generated by VirtualHip enable doctors to visually demonstrate specific issues within the hip joint, fostering better patient understanding and compliance with prescribed treatments, particularly among younger demographics.
Looking ahead, the VirtualHip project continues to evolve, with ongoing efforts to develop a patient-centric platform utilizing advanced language models and generative AI for personalized analyses and tailored treatment recommendations, further enhancing patient outcomes and experiences.