Artificial intelligence (AI), a technology that instills fear in most Americans, is actively utilized by all major hospital systems in Cincinnati.
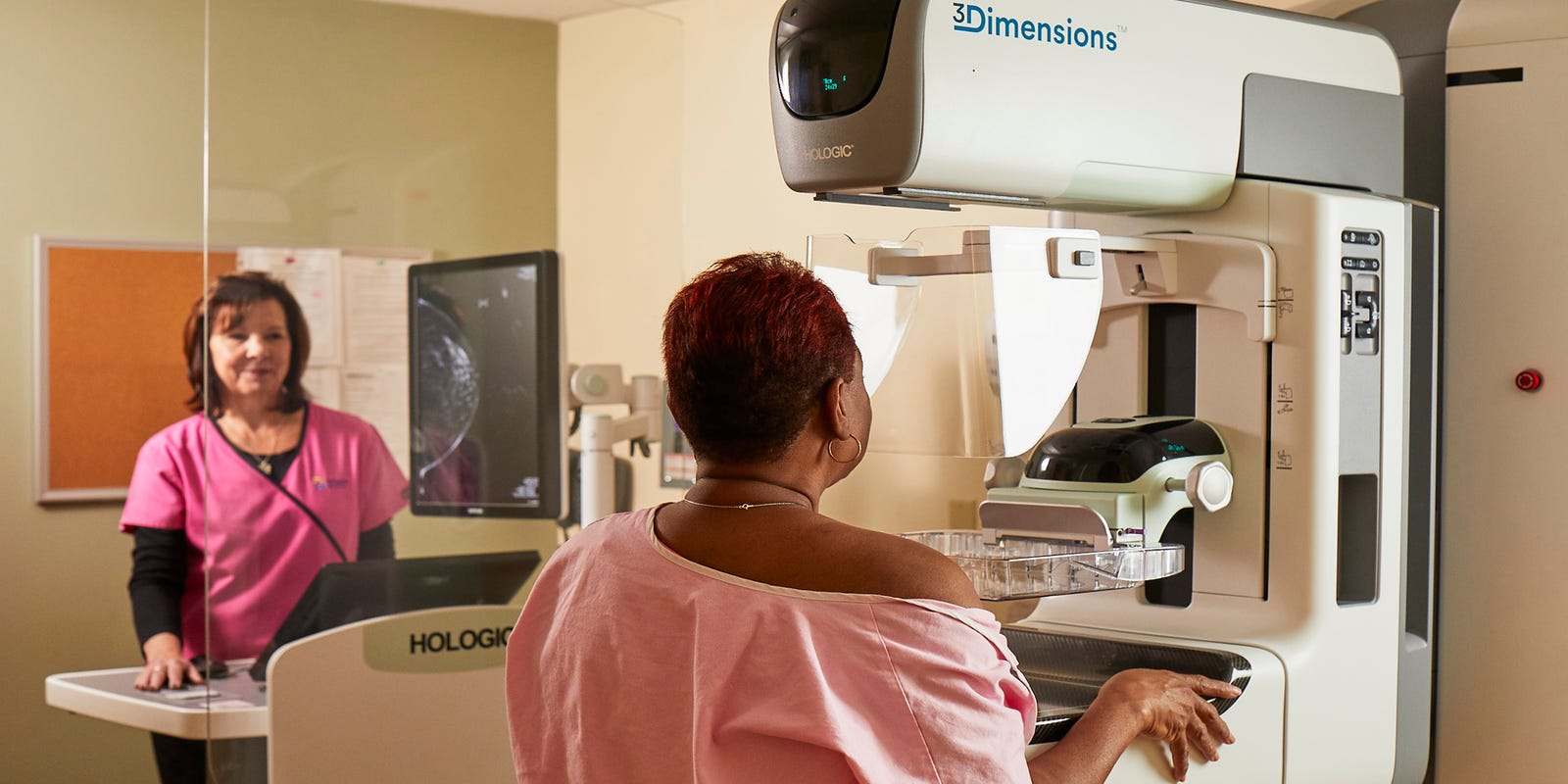
Trusted by TriHealth in Cincinnati, AI, also known as unnatural intelligence, plays a pivotal role in diagnosing critical conditions like breast cancer, stroke, and pulmonary edema, emphasizing the significance of early detection in prevention.
UC Health and St. Elizabeth leverage AI for monitoring and analysis, while Bon Secours Mercy Health relies on this technology to recruit nurses. In contrast, Christ Hospital partners with 3M’s AI for efficient plan and claim accounting management.
Despite the widespread integration of AI in healthcare systems, a 2023 Pew Research survey reveals a lack of trust among Americans towards this technology, with less than 40% anticipating positive impacts on patient health outcomes.
Notably, insurance companies have faced legal challenges nationwide due to the utilization of flawed AI systems. Moreover, healthcare providers using ChatGPT for generating health records have raised concerns about potential privacy breaches.
Hospital executives advocate for AI’s role in enhancing patient care and operational efficiency, aligning with the National Institutes of Health’s definition of synthetic intelligence as machines learning to perform tasks.
Christ Hospital’s collaboration with Microsoft and Epic Systems aims to develop AI facilitating personalized email responses for physicians, ensuring efficient communication. The hospital’s Chief Information Officer, Paul Grone, highlights AI’s evolution since the 1950s and its transformative impact on healthcare operations.
Embracing AI technology, TriHealth’s Chief Operating Officer, Terri Hanlon-Bremer, emphasizes its ability to streamline physicians’ workflows and enhance patient care without replacing the human element in medical decision-making.
TriHealth’s senior vice president, John Ward, contemplates implementing a ChatGPT-like system to assist doctors in addressing individual queries, acknowledging the challenges posed by the influx of digital messages in healthcare settings.
The adherence to HIPAA regulations is paramount in AI-driven healthcare initiatives to safeguard patient data. TriHealth’s emphasis on de-identifying information underscores the commitment to privacy and compliance.
As the healthcare sector navigates AI integration, vetting credible AI suppliers remains a critical task to ensure sustained technological support and clinical advancements.
The skepticism among Americans regarding AI’s benefits contrasts with hospital administrators’ optimism, reflecting concerns over the rapid adoption of AI systems in healthcare without adequate consideration of individual challenges.
Calls for stringent regulations on AI applications in healthcare echo across medical professionals and policymakers, underscoring the need for comprehensive data privacy policies to address ethical and privacy implications.
While the FDA is yet to approve AI resources for healthcare applications, industry experts foresee a future where generative AI becomes indispensable for competitive healthcare systems, emphasizing the need for ethical AI practices and patient protections.