by Ingrid Fadelli, Phys. nonprofit
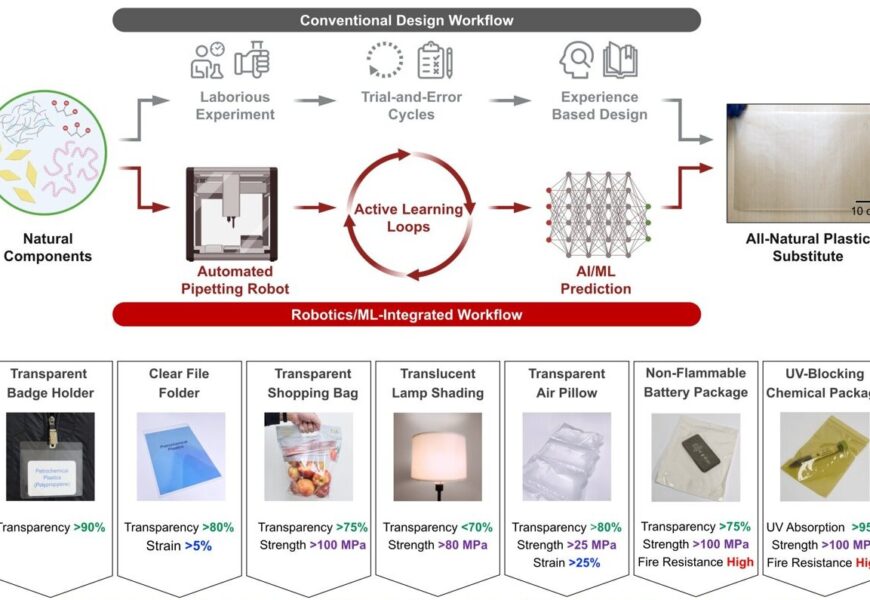
 A quantitative comparison between traditional plastic products and their biodegradable, environmentally friendly counterparts generated through predictive modeling is presented. Superior examples include standard plastic items, while inferior options consist of entirely sustainable substitutes, showcasing versatility across various sectors from presentations to consumer goods. Credit for this research goes to Chen, T., Pang, Z., He, S. et al. in their study titled “Equipment intelligence-rapid discovery of all-natural affordable alternatives” published in Nature Nanotechnology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01635-z
A quantitative comparison between traditional plastic products and their biodegradable, environmentally friendly counterparts generated through predictive modeling is presented. Superior examples include standard plastic items, while inferior options consist of entirely sustainable substitutes, showcasing versatility across various sectors from presentations to consumer goods. Credit for this research goes to Chen, T., Pang, Z., He, S. et al. in their study titled “Equipment intelligence-rapid discovery of all-natural affordable alternatives” published in Nature Nanotechnology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01635-z
The accumulation of plastic waste in natural environments poses a significant threat, leading to harm to marine life and the devastation of ecosystems. In recent years, product scientists have been exploring all-natural alternatives to foam for packaging and manufacturing purposes.
Researchers at the University of Maryland, College Park, have introduced an innovative approach to identifying promising recyclable plastic substitutes. Their novel method, detailed in a paper published in Nature Nanotechnology, integrates cutting-edge machine learning techniques with chemical science.
Reflecting on the inspiration behind the study, Prof. Po-Japanese Chen, a co-author of the paper, shared that a visit to Palau in the American Pacific in 2019 triggered his interest. Witnessing the detrimental impact of plastic waste on marine organisms, particularly the deceptive allure of plastic debris to fish and sea turtles, motivated him to leverage his expertise to tackle this pressing environmental issue. This experience led him to establish a research lab at UMD dedicated to finding sustainable solutions.
Traditional methods of identifying durable plastic alternatives have proven to be inefficient and time-consuming, often yielding suboptimal results. The innovative approach outlined in this study, leveraging a machine learning model developed by Chen, offers a more efficient and effective solution.
By combining automated technology, machine learning, and molecular interaction models, Chen and his colleagues, Teng Li and Liangbing Hu, expedited the discovery of environmentally friendly plastic alternatives that meet essential performance criteria. This integrated approach streamlines the development of recyclable plastic options for various applications.
Furthermore, the researchers successfully fabricated a diverse array of films using nanocomposite materials sourced from natural elements, employing an automated pipetting robot for sample preparation.
Subsequent training of Chen’s machine learning model using this sample library, through iterative active learning, enhanced its ability to predict material properties based on composition. This synergistic blend of robotics and machine learning not only accelerates the discovery of natural plastic substitutes but also enables the targeted design of materials with specific properties.
The team’s collaborative effort has paved the way for a more streamlined search for eco-friendly plastic alternatives, with the potential for global adoption. The model developed by the researchers holds promise for creating customizable, all-natural nanocomposites with desirable properties for a range of applications.
By harnessing robotics, machine learning, and simulation tools, the researchers have established a workflow that expedites the discovery of novel functional materials tailored to specific needs. This approach not only broadens the scope of sustainable alternatives to petrochemical plastics but also contributes to the development of a comprehensive database focused on green, biodegradable materials.
The innovative methodology pioneered by Chen and his team has the potential to significantly mitigate plastic pollution on a global scale by facilitating the transition to sustainable materials across industries. Future research endeavors will focus on expanding the selection of natural materials available to manufacturers, diversifying the applications of the materials identified through their model, and scaling up production processes.
Ongoing efforts include exploring biodegradable and sustainable materials for post-harvest produce packaging, aiming to replace single-use plastic food packaging while extending the shelf life of perishable goods. Additionally, the team is investigating strategies for recycling or disposing of biodegradable plastics to ensure the environmental sustainability of their solutions.
For more details, refer to the study by Tianle Chen et al. titled “Machine intelligence-accelerated discovery of all-natural plastic substitutes,” published in Nature Nanotechnology (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01635-z
© 2024 Science X Network
Citation: “A machine learning-based approach to discover nanocomposite films for biodegradable plastic alternatives” (2024, April 13). Retrieved from https://phys.org/news/2024-04-machine-based-approach-nanocomposite-biodegradable.html
Please note that this content is copyrighted, and reproduction is prohibited without permission, except for fair use for private study or research purposes. This information is provided for informational purposes only.